

- #MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE PATCH#
- #MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE PRO#
- #MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE WINDOWS 7#
- #MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE WINDOWS#
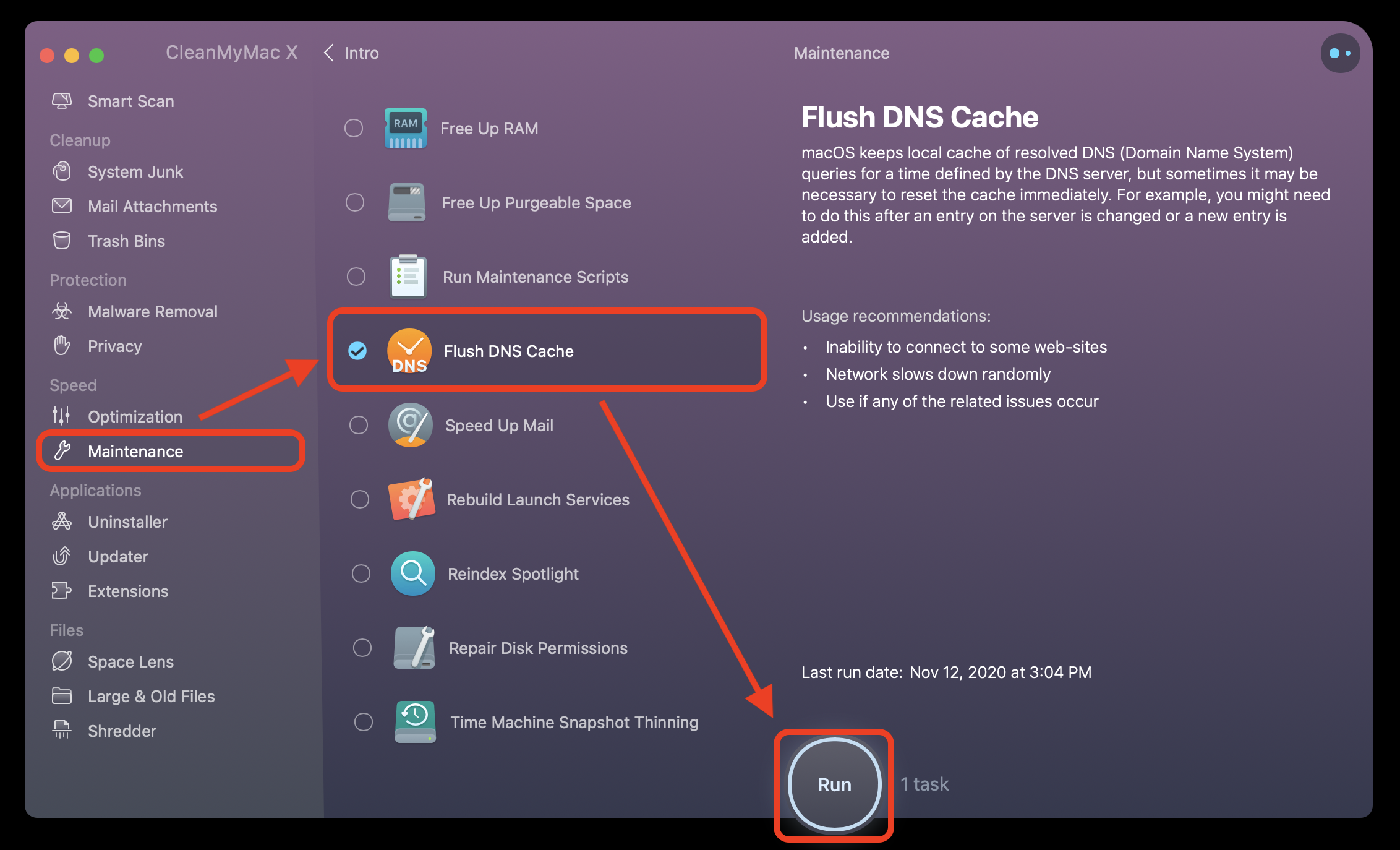
Many end users don’t realize that DNS caches can be intercepted by hackers. Security is an important reason to flush your DNS cache. Just clearing the DNS cache can often solve this dilemma. DNS Server Not Responding Errorsįlushing your DNS cache can also help with common connectivity errors such as “DNS server not responding.” If a provider or domain isn’t experiencing an outage or DNS-related issue, there’s a strong chance that the problem is on the client side.

Clearing your web browser cache can help with this as well, but isn’t always enough. It can also cause websites to display incorrectly or show old images and text. This can cause certain sites or applications to misbehave. DNS Record Propagationīecause it can take time for DNS record updates to propagate across all servers worldwide-as long as 24-48 hours in some cases-information in cache can become outdated. The most common of which is to ensure information in your local cache is up-to-date, for troubleshooting DNS errors when trying to access certain sites, and for protection from DNS cache poisoning and spoofing. There are several reasons to flush your DNS cache every so often. Once TTL has expired for a record, changes need to propagate globally, across all servers, and the entire lookup process begins again. Any recently visited site is cached until time to live (TTL) for the domain’s DNS records have expired. This usually involves several different servers (recursive, root, top-level domain (TLD), and authoritative nameservers), but client-side (your device) requests can also be answered by your browser or the recursive resolver if the information requested is in cache.Ī DNS cache is like a memory bank for website information. What is DNS Caching and How Does it WorkĪnytime you enter a URL into your web browser, a DNS lookup process is initiated. This applies whether you are using a home or office computer.
#MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE WINDOWS#
You’ll also learn the commands to clear your local DNS cache for Windows and Mac. In this blog, I’ll be covering what DNS cache is, how it works, and why you should flush it. So, wit.Flushing your DNS cache is an easy and helpful way to troubleshoot DNS and connectivity errors, as well as keeping your local cache more secure. I'm always asking "What did you play this weekend" and never "What do you want to play this weekend" but not only that what do you want to do in general?Me? Well, I firmly believe the weekend starts on Friday, but specifically after you clock out.
#MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE PRO#
#MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE PATCH#
We have a lot of updates and none more relevant than Microsoft since their AD Authentication issues from last week's patch Tuesday. Good morning and welcome to today's briefing.
# Please Configure the following variables. It checks AD nightly on a scheduled task for accounts with an upcoming expiry date and emails the user to warn them to change their password. We use a powershell script that I found somewhere.
#MAC OS ACTIVE DIRECTORY PASSWORD CACHE WINDOWS 7#
Server OS: Windows Server 2008 R2, Client OS: Windows 7 Pro Or is the user allowed to continue using the expired password to log into his laptop while not on the domain network.as the laptop OS will have no way of knowing that the password is expired?Īnd how do the cached credentials (if any) come into play? Is the password expiry policy reflected in the laptop's registry or local GPO? Meaning that it will lock him out even while abroad? This is obviously a scary situation, as if they are not on the company network/domain then the password cannot be reset. In an Active Directory domain, with a password expiry policy, if one of the users with a domain-joined laptop leaves the office for some time, and during that time the password expires (it reached its 30-day limit), what happens to the user/laptop? My colleagues and I were discussing a possible problem/situation that may arise in a Windows domain.simple question really:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
